DR SACHIN VIJAY NAIKNAWARE. GYNAEC LAPAROSCOPIC SURGEON, MUMBAI,INDIA.
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Adnexal torsion is the 5th most common gynaecological emergency occurring in about 2-15% of all reproductive age group womens wherein both fallopian tube and ovary twists along the vascular pedicle which causes obstruction to venous outflow and arterial inflow.clinical presentation of adnexal torsion is highly variable and physical examination is often inconclusive. early diagnosis increases the chances of saving the ovary and preventing life threatening complications such as thrombophlebitis and peritonitis.
Torsion most commonly involve both fallopian tube and ovary ,isolated ovarian torsion is a rare entity occurring in about 1 to 1.5 million womens. it is most common in reproductive age group women and during pregnancy and is less common in pre menarche and in postmenopausal women.twisting of ovarian pedicle initially obstruct venous flow causing engorgement and ovarian oedema and this engorgement progrese causing arterial blood flow obstruction and finally schema and necrosis of ovarian tissues.
Ovarian torsion is likely to occur when there is some problem with ovary as in ovarian cyst causing enlargement, pregnancy, hormonal medication use for ovulation induction and sometimes normal ovaries can twist in children. torsion can either be intermittent or complete causing sudden onset of severe abdominal pain. it is found that more than 80% of patients with torsion has ovarian mass of =>5cm in size and enlarged ovaries, it is also found that benign tutors more likely to get tossed than the malignant tumors. of all the cases of torsion 10-20 % ovarian torsion cases occur during pregnancy and most cases found around 10-17 weeks of pregnancy.
Clinically these patients are presented with sudden onset of severe abdominal or pelvic pain which may be localised to lower abdomen, nausea or vomiting, low grade fever and tachycardia, and on abdominal examination it may reveal abdominal tenderness and localised guarding or rigidity.
Various other diseases may mimic the ovarian torsion such as pelvic inflammatory disease,appendicitis, renal colic, ectopic pregnancy and ovarian cysts.
Accurate diagnosis of ovarian torsion can be reached by appropriate history taking and clinical examination, per abdominal and per vaginal examination as the case may be, ultrasound including colour doppler examination, sometimes ct scan and MRI scan may also be required , laparoscopy help in accurately diagnosing and treating the condition in same sitting.
Various treatment modalities are used for treating adnexal torsion , treatment during pregnancy and in childhood may differ as there is no uniform criteria for the management of adnexal torsion. many observational studies found that detorsion is associated with preserved ovarian function. as there is no guidelines for the management various questions may arise as whether to do only detorsion ? when and at what size of ovarian cyst with torsion do we do cystectomy? or when to do utero ovarian ligament plication and which modality to be used in premenarcheal girls. to answer all these questions this management criteria is proposed to objectively form the guidelines that can be considered while operating on adnexal torsion cases.
proposed dr sachin’s criteria:-
- if torsion + ovarian cyst =>5cm do ovarian cystectomy.
- if utero-ovarian ligament =>5cm do ligament plication.
- pre-menarche torsion or in recurrent torsion use ‘HOT DOG IN BUN’ technique.
- if prod + torsion do prod drilling + ligament plication +ovarian suppression for 6 months.
How to measure utero- ovarian length objectivaly ?
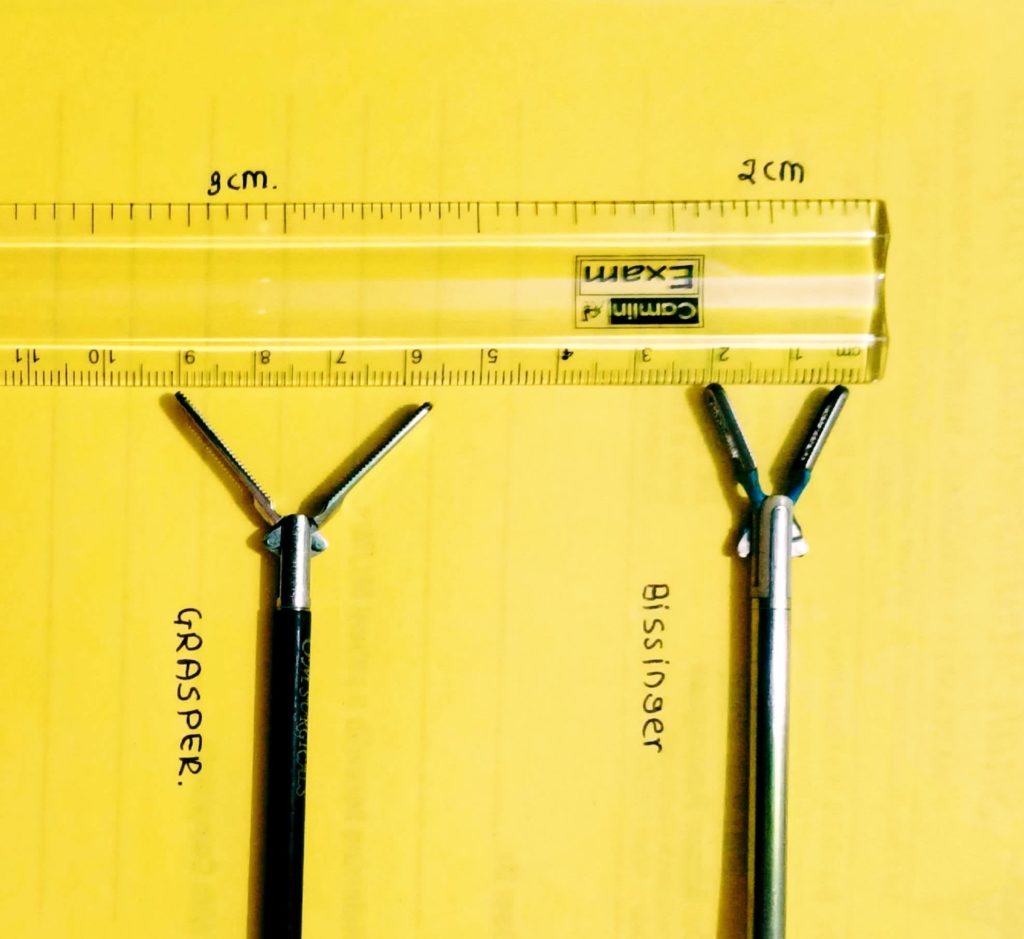

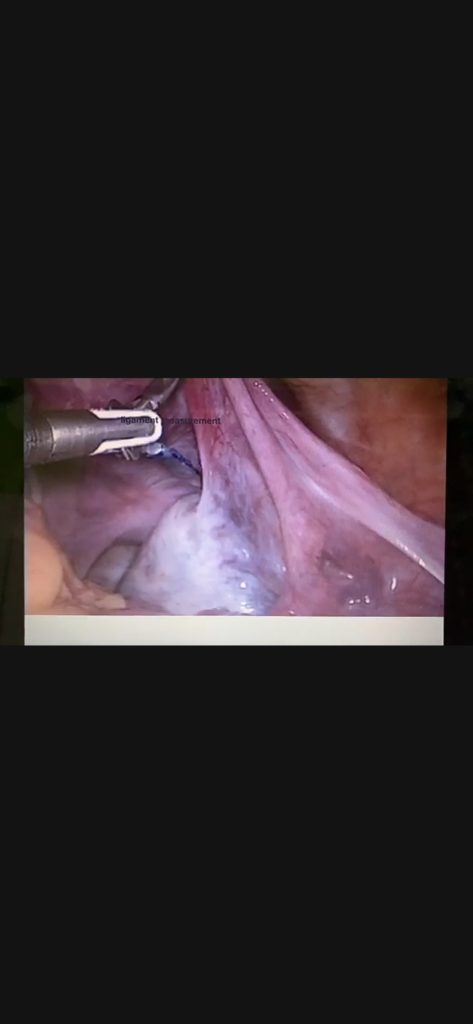
Bipolar forces and bows graspers are two commonly used instrument by any laparoscopic surgeons by using 1 of the available we use the length objectively. length between open jaws of bissinger is 2cm and that of bowel grasper is 3cm so we can measure the utero-ovarian length or ovarian cyst size.
As at present there is no objective criteria or near cut guidelines this approach can help laproscopic surgeons to standardise the management protocols and to compare the results. to get is accepted at large scale some more case studies are required, till then it can be used as guiding stone in a standardised way to manage the patient with adnexal torsion.
